What Is SVC in Telecom? Switched Virtual Circuit Explained
SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit) is a temporary, on-demand network connection, its types, benefits, and real-world use in telecom networks are explained.
Author: Sujith Grandhi
SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit) is a temporary, on-demand network connection, its types, benefits, and real-world use in telecom networks are explained.
Author: Sujith Grandhi
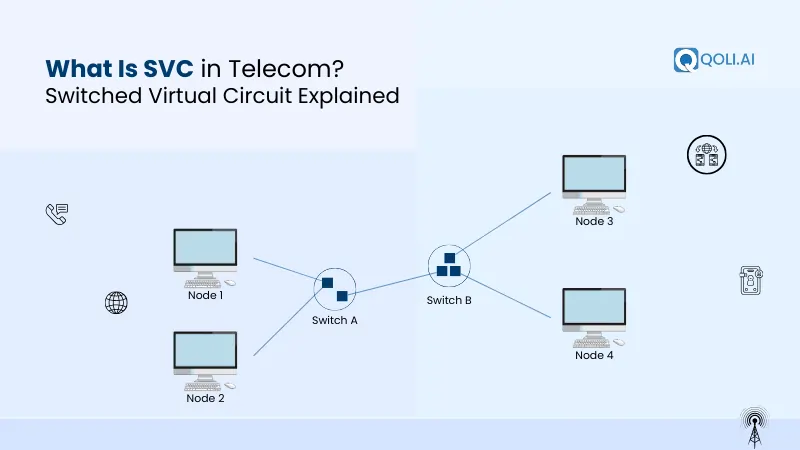
SVC is a temporary network connection established on demand. Unlike a Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC), it exists only while data is being transmitted, making it flexible and cost-efficient for telecom networks.
SVC stands for Switched Virtual Circuit.
In telecommunications, an SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit) is a temporary, on-demand network connection that exists only for the duration of a data session. Unlike permanent connections, it is established only when data needs to be transmitted and automatically disconnects once the transmission is complete.
Think of it like a dialled phone call — the connection is active while you’re communicating and disappears afterwards. This approach allows networks to provide a dedicated path for data without reserving resources all the time, making SVC flexible, cost-efficient, and efficient in bandwidth usage.
SVC is commonly used in telecom networks, enterprise systems, and ATM networks, where connections are needed temporarily rather than continuously. Its on-demand nature ensures that network resources are optimised while still giving the reliability of a point-to-point connection.
Switched Virtual Circuits are mainly classified into two types based on how data is transmitted:
1. Circuit-Switched SVC
2. Packet-Switched SVC
These types allow networks to choose the best approach depending on the application and traffic needs.
Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC) and Permanent Virtual Circuit (PVC) are both virtual connections, but they work differently:
| Feature | SVC (Switched Virtual Circuit) | PVC (Permanent Virtual Circuit) |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Temporary, on-demand | Permanent, always active |
| Resource Usage | Uses network resources only during a session | Resources reserved continuously |
| Flexibility | High, connection created as needed | Low, always fixed |
| Cost | Lower for occasional use | Higher due to continuous allocation |
In short:
SVC is ideal for situations where connections are needed occasionally, ensuring efficient use of network resources without sacrificing reliability.